Are Acids Ionic Or Molecular
4.7: Which Bonds are Ionic and Which are Covalent?
- Page ID
- 191160
Cells incorporate lots of water. One of the roles of the water is to dissolve unlike materials. For instance, there are many different ionic compounds (salts) in cells. Ions are used to maintain cell potentials and are of import in jail cell signaling and muscle contraction.
How tin yous tell if a chemical compound is ionic or covalent?
There is not a simple answer to this question. Many bonds are somewhere in betwixt. In a polar covalent bond, a pair of electrons is shared between 2 atoms in society to fulfill their octets, just the electrons prevarication closer to one end of the bond than the other. In that location is more negative charge toward i end of the bond, and that leaves more positive accuse at the other end.
Looking at the electronegativity values of different atoms helps us to make up one's mind how evenly a pair of electrons in a bail is shared. Electronegativity increases toward the upper correct hand corner of the periodic table because of a combination of nuclear accuse and shielding factors. Atoms in the upper correct hand corner of the periodic tabular array accept a greater pull on their shared bonding electrons, while those in the lower left paw corner have a weaker attraction for the electrons in covalent bonds.
In a carbon-oxygen bond, more than electrons would be attracted to the oxygen because it is to the right of carbon in its row in the periodic tabular array. Compounds like , dimethyl ether, CH3OCH3, are a little flake polar. Formaldehyde, CHtwoO, is even more polar. Electrons in pi bonds are held more loosely than electrons in sigma bonds, for reasons involving quantum mechanics. That allows the oxygen to pull the electrons toward it more hands in a multiple bail than in a sigma bond.

Not all polarities are like shooting fish in a barrel to determine by glancing at the periodic table. The management of the dipole in a boron-hydrogen bond would exist difficult to predict without looking up the electronegativity values, since boron is farther to the right but hydrogen is college up. Every bit it turns out, the hydrogen is slightly negative.
A bond is ionic if the electronegativity departure between the atoms is not bad plenty that one atom could pull an electron completely away from the other ane. That situation is common in compounds that combine elements from the left-hand edge of the periodic tabular array (sodium, potassium, calcium, etc.) with elements in the extreme upper right hand corner of the periodic tabular array (most commonly oxygen, fluorine, chlorine). Sodium chloride is an ionic chemical compound.
Many bonds can be covalent in one situation and ionic in another. For instance, hydrogen chloride, HCl, is a gas in which the hydrogen and chlorine are covalently spring, but if HCl is bubbled into water, it ionizes completely to give the H+ and Cl- of a hydrochloric acid solution. Even in gaseous HCl, the charge is not distributed evenly. The chlorine is partially negative and the hydrogen is partially positive.
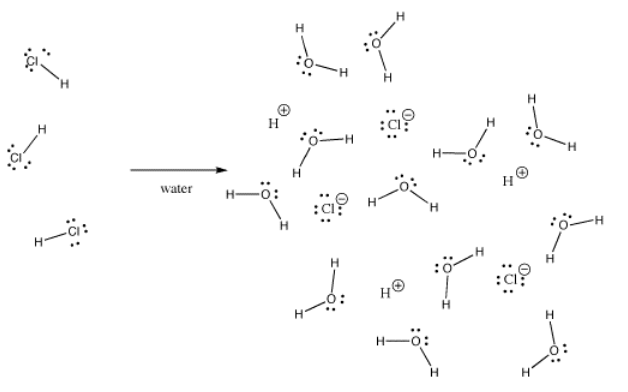
Potassium hydroxide, KOH, contains one bail that is covalent (O-H) and 1 that is ionic (One thousand-O). Hydrogen is tricky because it is at the top of the periodic table as well as the left side. It is just electropositive enough to grade ionic bonds in some cases. Information technology is just electronegative enough to class covalent bonds in other cases.
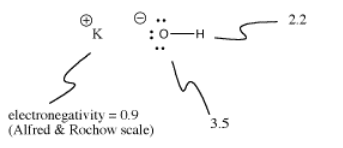
In KOH, the K-O bond is ionic because the difference in electronegativity between potassium and oxygen is large. The deviation in electronegativity between oxygen and hydrogen is not small. An O-H bond can sometimes ionize, but non in all cases.
Sometimes ionization depends on what else is going on within a molecule. Considering the K-O bond in potassium hydroxide is ionic, the O-H bail is not very likely to ionize. At that place is already a negative charge on oxygen. Accuse separation costs free energy, then it is more difficult to put a 2d negative charge on the oxygen by ionizing the O-H bond as well. Frequently offset ionizations in molecules are much easier than second ionizations.
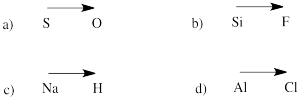
Predict the management of polarity in a bond between the atoms in the post-obit pairs:
a) sulfur-oxygen b) silicon-fluorine
c) hydrogen-sodium d) chlorine-aluminum
- Reply
-
Because it is so common that an chemical element from the extreme left paw of the periodic table is nowadays every bit a cation, and that elements on the farthermost right carry negative charge, we can often presume that a compound containing an example of each volition have at to the lowest degree i ionic bond.
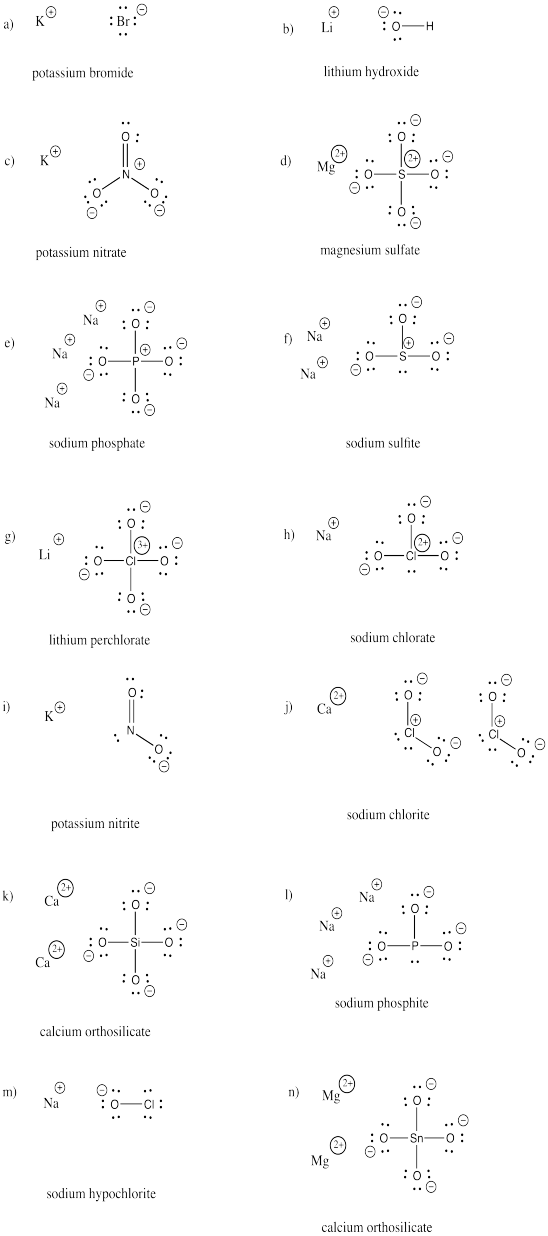
Draw structures of the following compounds. Each one contains at least one anion and cation.
a) KBr b) LiOH c) KNOthree d) MgSOiv due east) NaiiiPOfour f) Na2SO3
1000) LiClO4 h) NaClOthree i) KNO2 j) Ca(ClO2)2 k) Ca2SiOfour l) Na3POiii
m) NaOCl n) MgtwoSnO4
- Answer
-
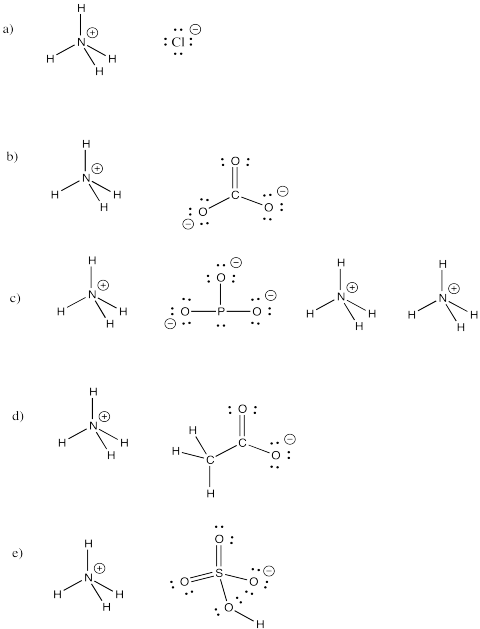
Ammonium ion, NH4 +, is a common molecular ion. Draw structures for the following compounds that include this ion.
a) NHivCl b) (NH4)2COthree c) (NH4)3PO3 d) NHfourCHiiiCOii e) NHivHSOfour
- Answer
-
Many anions accept names that tell you something about their structure.
| prefix- or -suffix | common meaning | example name | example formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| -ide | atom is present as anion | chloride | Cl - |
| -ate | atom is present as an oxyanion; usually a common class | chlorate | ClOiii - |
| -ite | cantlet is present as an oxyanion, but with fewer oxygens (or lower "oxidation state") than another common form | chlorite | ClO2 - |
| per- | atom is present as an oxyanion, only with even more oxygens than the "-ate" course | perchlorate | ClOiv - |
| hypo- | cantlet is present as an oxyanion, only with fifty-fifty fewer oxygens than the "-ite" form | hypochlorite | ClO- |
Using the table as a guide, propose names for the following anions:
a) Br- b) O2- c) F- d) CO3 ii - (common oxyanion) e) NOiii - (mutual oxyanion) f) NO2 -
g) Southward2- h) Then4 2 - (common oxanin) i) And theniii 2 - j) And then5 ii - m) Civ- l) N3- m) As3 -
north) PO4 3 - (mutual oxyanion) o) PO3 three - p) I- q) IOthree - (mutual oxyanion) r) IO4 -
- Respond a
-
bromide
- Respond b
-
oxide
- Answer c
-
fluoride
- Answer d
-
carbonate
- Reply e
-
nitrate
- Answer f
-
nitrite
- Answer g
-
sulfide
- Answer h
-
sulfate
- Answer i
-
sulfite
- Answer j
-
persulfate
- Reply k
-
carbide
- Answer l
-
nitride
- Answer m
-
arsenide
- Answer north
-
phosphate
- Answer o
-
phosphite
- Answer p
-
iodide
- Reply q
-
iodate
- Answer r
-
periodate
Are Acids Ionic Or Molecular,
Source: https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/General_Chemistry/Book%3A_Structure_and_Reactivity_in_Organic_Biological_and_Inorganic_Chemistry_(Schaller)/I%3A__Chemical_Structure_and_Properties/04%3A_Introduction_to_Molecules/4.07%3A_Which_Bonds_are_Ionic_and_Which_are_Covalent
Posted by: murraynessittere.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Are Acids Ionic Or Molecular"
Post a Comment